|
Royal Navy`s D class, first British submarine with Diesel engines
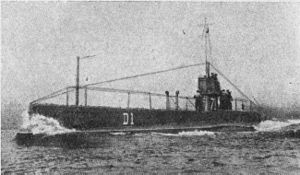 D class submarines were the first British boats to fitted with diesel engines, be designed for overseas patrols, to have twin screw, saddle tanks and full deck casing. The larger conning tower also indicated a break from former designs; they also featured an upper and lower rudder. The upper rudder was not successful and was prone to damage from wave action on the surface so it was removed at an early date. Another innovation was the ability to transmit and receive radio messages although the aerial had to be erected by hand. These were the last British built boats without transverse watertight compartments. D class submarines were the first British boats to fitted with diesel engines, be designed for overseas patrols, to have twin screw, saddle tanks and full deck casing. The larger conning tower also indicated a break from former designs; they also featured an upper and lower rudder. The upper rudder was not successful and was prone to damage from wave action on the surface so it was removed at an early date. Another innovation was the ability to transmit and receive radio messages although the aerial had to be erected by hand. These were the last British built boats without transverse watertight compartments.
Specifications, HMS D-1, D class:
Keel laid down by Vickers Sons & Maxim Ltd in Barrow-in-Furness; launched May 16, 1908
Displacement (srf/sub tons): 483/595
Dimensions (L*B*D feet): 126`3*15`9*8`1
Propulsion: 2*600hp 6-cylinder Vickers diesel engine, 2*275hp electric motors for submergence driving two shafts
Speed (srf/sub knots): 14/10
Range (srf/sub n/miles@knots): 2,500@10/un known
Diving depth (feet): 100
Complement: 3 officers 22 enlisted
Torpedo: 2*18" bow torpedo tube, 1*18" stern torpedo tube, containing a total of 6 torpedoes
Mines: none
Armament: 1*12pdr main deck gun added later
Construction
The eight submarines of the D class (D-1 to D-8) were launched between 1908 and 1911. They were the first British submarines with diesel engines and twice as big as their predecessors of the C class. This construction also increased the range and comfort of the crew.
Only 8 submarines of this design were ever built, 6 by Vickers Sons & Maxim Ltd in Barrow-in-Furness, D-7 and D-8 were built by Chatham Dockyard.
Back to History Index
 |
Liberia |
2001 |
D-1,built September 1909 by Vickers.First sub' fitted with diesel engin |
|